3.Write a Java program to create a class called Shape with a method called getArea(). Create a subclass called Rectangle that overrides the getArea() method to calculate the area of a rectangle.
💡Code:
// Shape class
class Shape {
public double getArea() {
return 0; // Default implementation for unknown shapes
}
}
// Rectangle subclass extending Shape
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double length;
private double width;
public Rectangle(double length, double width) {
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return length * width; // Calculate area of rectangle
}
}
class Inheritance3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape shape = new Shape(); // Creating an instance of Shape (will use default getArea())
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(20, 40); // Creating an instance of Rectangle
double rectangleArea = rectangle.getArea(); // Calculating area of rectangle
System.out.println("Area of a shape (default): " + shape.getArea());
System.out.println("Area of a rectangle: " + rectangleArea);
}
}
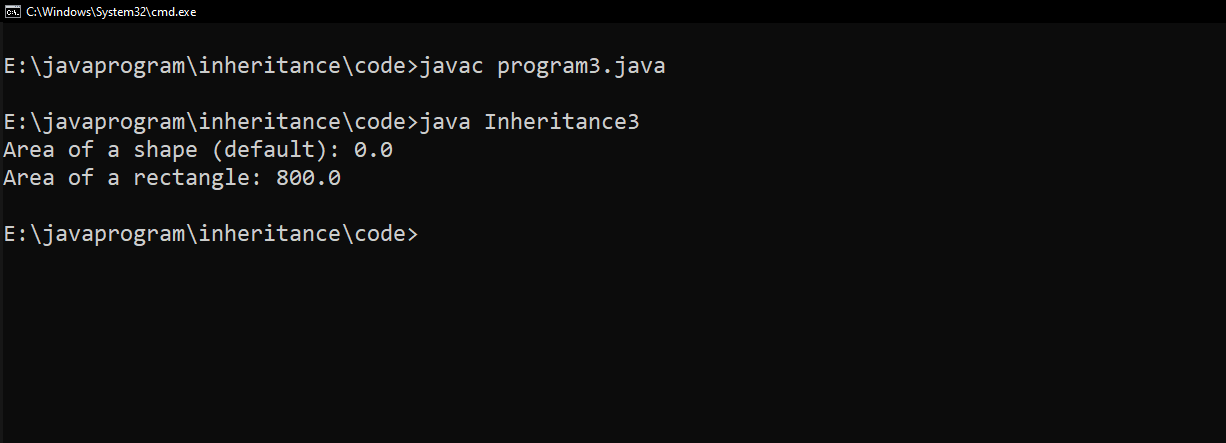
📸Output :