4.Write a Java program to create a class called Employee with methods called work() and getSalary(). Create a subclass called HRManager that overrides the work() method and adds a new method called addEmployee().
💡Code:
// Employee class
class Employee {
private double salary;
public Employee(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public void work() {
System.out.println("Employee is working...");
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
}
// HRManager subclass extending Employee
class HRManager extends Employee {
public HRManager(double salary) {
super(salary);
}
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("HR Manager is working...");
}
public void addEmployee() {
System.out.println("HR Manager is adding a new employee...");
}
}
class Inheritance4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee emp = new Employee(6000); // Creating an instance of Employee
HRManager hrManager = new HRManager(7500); // Creating an instance of HRManager
emp.work(); // Calling work() for Employee
System.out.println("Employee Salary: " + emp.getSalary());
System.out.println();
hrManager.work(); // Calling work() for HRManager (overridden method)
System.out.println("HR Manager Salary: " + hrManager.getSalary());
hrManager.addEmployee(); // Calling addEmployee() for HRManager (specific method)
}
}
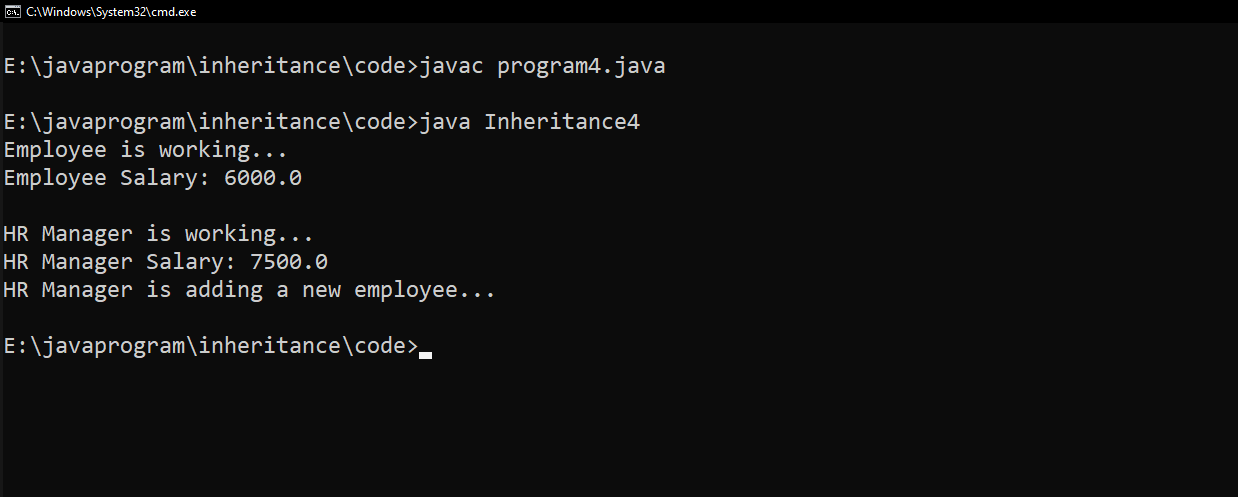
📸Output :