1. 1. Write a Java program to create an interface Shape with the getArea() method. Create three classes Rectangle, Circle, and Triangle that implement the Shape interface. Implement the getArea() method for each of the three classes.
💡Code:
// Shape interface
interface Shape {
double getArea();
}
// Rectangle class implementing Shape
class Rectangle implements Shape {
private double length;
private double width;
public Rectangle(double length, double width) {
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return length * width;
}
}
// Circle class implementing Shape
class Circle implements Shape {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
// Triangle class implementing Shape
class Triangle implements Shape {
private double base;
private double height;
public Triangle(double base, double height) {
this.base = base;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return 0.5 * base * height;
}
}
// Main class to test the Shape interface and its implementations
class ShapeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test Rectangle
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(5, 8);
System.out.println("Area of Rectangle: " + rectangle.getArea());
// Test Circle
Circle circle = new Circle(4);
System.out.println("Area of Circle: " + circle.getArea());
// Test Triangle
Triangle triangle = new Triangle(6, 10);
System.out.println("Area of Triangle: " + triangle.getArea());
}
}
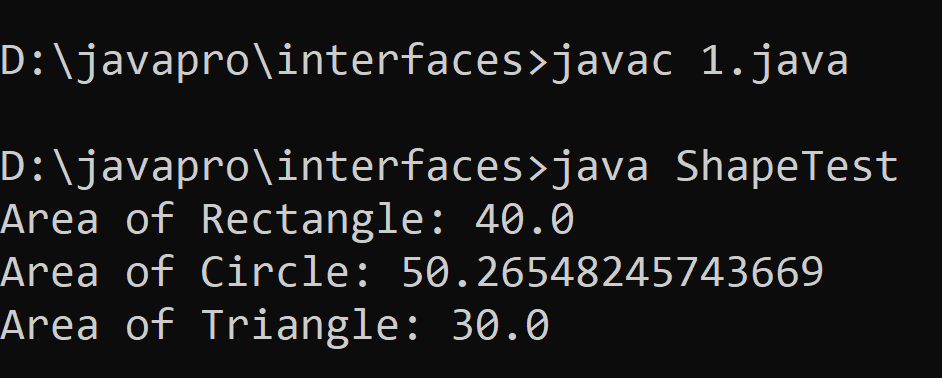
📸Output :