7. Write a Java program to create an interface Sortable with a method sort() that sorts an array of integers in ascending order. Create two classes BubbleSort and SelectionSort that implement the Sortable interface and provide their own implementations of the sort() method.
💡Code:
interface Sortable {
void sort(int[] arr);
}
class BubbleSort implements Sortable {
@Override
public void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
boolean swapped;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
swapped = false;
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
// Swap arr[j] and arr[j+1]
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no two elements were swapped in inner loop, the array is already sorted
if (!swapped) {
break;
}
}
}
}
class SelectionSort implements Sortable {
@Override
public void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
// Swap the found minimum element with the first element
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
public class SortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
Sortable bubbleSort = new BubbleSort();
bubbleSort.sort(arr);
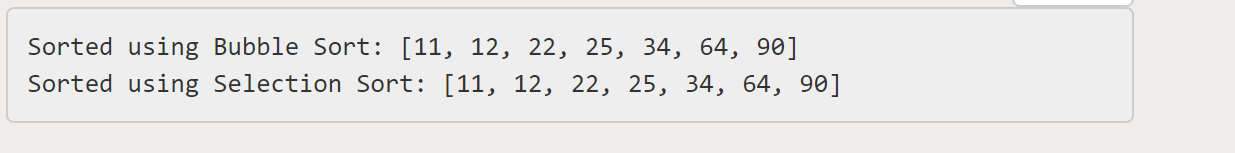
System.out.println("Sorted using Bubble Sort: " + java.util.Arrays.toString(arr));
int[] arr2 = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
Sortable selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
selectionSort.sort(arr2);
System.out.println("Sorted using Selection Sort: " + java.util.Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
📸Output :